Nerif Core
Core component in Nerif project is nerification, nerif and nerif_match.
Nerification
Nerification := Not only Verification
Base class: NerificationBase
This class is used to verify the result of the Nerif. This class provides base functionality for verifying and matching values against a predefined set of possible values.
Attributes:
original_options (List[Any]): Original list of possible values before conversionpossible (List[str]): List of possible values converted to lowercase stringsembedding (SimpleEmbeddingModel): Model used for generating embeddings
Methods:
-
convert(val: Any) -> str: Converts a value to lowercase string format -
verify(val: Any) -> bool: Checks if a value exists in the possible values list -
simple_fit(val: Any): Uses embeddings to find the closest matching possible value -
force_fit(val: Any, similarity="cosine"): Uses embeddings to find the closest matching possible value
Based on the base method, we implement different value check strategy:
Nerification, NerificationInt and NerificationString
Example:
from nerif.core import Nerification
from nerif.core import NerificationInt
from nerif.core import NerificationString
nerification = Nerification(model="text-embedding-3-large")
print(nerification.simple_fit("yes, it is"))
# result: None
print(nerification.force_fit("yes, it is"))
# result: True
print(nerification.simple_fit("true"))
# result: True
print(nerification.force_fit("true"))
# result: True
nerification_int = NerificationInt(model="text-embedding-3-large", possible_values=[1, 233, 343])
print(nerification_int.simple_fit(1))
# result: 1
print(nerification_int.force_fit(1))
# result: 1
print(nerification_int.simple_fit(233))
# result: 233
print(nerification_int.force_fit("The value is 233"))
# result: 233
print(nerification_int.simple_fit(343))
# result: 343
print(nerification_int.force_fit("The value is 343"))
# result: 343
nerification_string = NerificationString(model="text-embedding-3-large", possible_values=["YES", "NO"])
print(nerification_string.simple_fit("yes"))
# result: YES
print(nerification_string.force_fit("Well, I guess you are right"))
# result: YES
print(nerification_string.simple_fit("no"))
# result: NO
print(nerification_string.force_fit("Oh, I don't think so"))
# result: NO
Nerif & Nerif Match
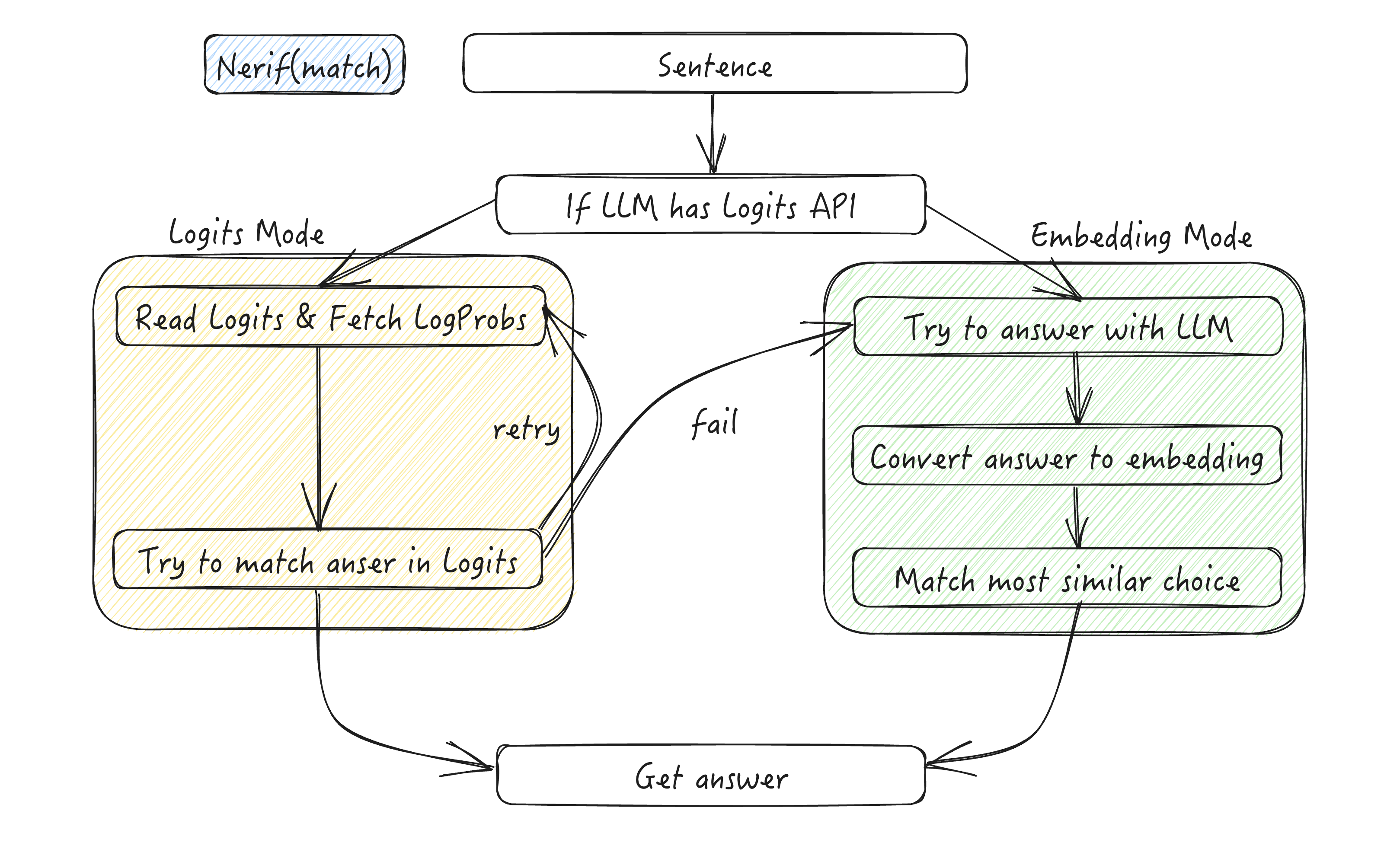
Overview
The Nerif and Nerif Match components provide robust mechanisms for controlling and interpreting LLM outputs. They address common challenges like overly verbose responses or inconsistent formatting by using a dual-mode approach: logits mode and embedding mode.
How It Works
LLM outputs can sometimes be unpredictable - they may include unnecessary pleasantries or irrelevant information. To handle this, we employ two strategies:
-
Logits Mode
- Uses the LLM's logits API to get top-k most probable token outputs
- Faster but may be less accurate
- Not available on all LLM services
-
Embedding Mode
- Activates if logits mode fails or is unavailable (You can also call embedding mode directly)
- Generates analysis of the input and compares embeddings with possible options
- More reliable but slower
- Guarantees a result in one attempt
The workflow diagram above illustrates this process.
Nerif Class
The Nerif class evaluates the truthfulness of statements using both logits and embedding modes.
Attributes:
model: str- LLM model name (default: NERIF_DEFAULT_LLM_MODEL)embed_model: str- Embedding model name (default: NERIF_DEFAULT_EMBEDDING_MODE)temperature: float- Model temperature, defaults to 0counter: Optional[NerifTokenCounter]- Token usage counterdebug: bool- Debug mode flag
Key Methods:
logits_mode(text: str) -> bool- Evaluates using logits analysisembedding_mode(text: str) -> bool- Evaluates using embedding comparisonjudge(text: str, max_retry: int = 3) -> bool- Main evaluation methodinstance(text: str, max_retry: int = 3, model: str = NERIF_DEFAULT_LLM_MODEL, debug: bool = False) -> bool- Creates and runs a new instance
Example:
Nerif Match Class
The Nerif Match class selects the best matching option from a list of choices.
Attributes:
choices: List[str]- Available options to match againstmodel: str- LLM model name (default: NERIF_DEFAULT_LLM_MODEL)embed_model: str- Embedding model name (default: NERIF_DEFAULT_EMBEDDING_MODEL)temperature: float- Model temperature, defaults to 0counter: Optional[NerifTokenCounter]- Token usage counter
Key Methods:
logits_mode(text: str) -> int- Matches using logits analysisembedding_mode(text: str) -> int- Matches using embedding comparisonmatch(text: str, max_retry: int = 3) -> int- Main matching methodinstance(choices: List[str], text: str, max_retry: int = 5, model: str = NERIF_DEFAULT_LLM_MODEL, embed_model: str = NERIF_DEFAULT_EMBEDDING_MODEL, debug: bool = False, counter: Optional[NerifTokenCounter] = None) -> int- Creates and runs a new instance
Example:
Instant Mode
Some times for a super fast use, we can start a instant mode. In Nerif project, we provide 2 function to simplify the API call: nerif and nerif_match.